HEPA FILTER
HEPA Filters
In an era punctuated by rising concerns about air quality and the harmful effects of pollution, the question of clean, breathable air is more pertinent than ever. Amidst this turbulent atmosphere, there exists a silent superhero, one who tirelessly works to protect us from invisible villains: the High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filter. Its versatility, adaptability and unrivaled efficiency make it one of the most indispensable tools we possess towards ensuring a healthier tomorrow.
A HEPA filter, characterized by its ability to trap 99.995% of particles greater than 0.3μm, is a marvel of engineering employing fine fiber glass as its main filtering component. Its construction, often using robust and lightweight materials like galvanized steel, stainless steel, aluminum, or plastic as its frame, is crafted to withstand a myriad of challenging conditions. The filter media, separated by aluminum or delicately crafted filter paper, all add to the undeniable efficacy of the HEPA filter.
One of the standout extensions of the HEPA filter is the Pleat and No Pleat HEPA filter designs. The Pleat HEPA, with its 99.99% efficiency achieved via the Sodium Flame method, is a timeless representative of high-efficiency filters. On the other hand, the No Pleat HEPA filters, specifically engineered as terminal filters for cleanrooms, achieve mind-boggling efficiencies up to 99.9995%, as measured by the MPPS method.
Still, the efficiency is but a fraction of what makes HEPA filters the unsung heroes of air filtration. Their lightweight construction belies a large filtration surface, enabling considerable dust holding capacity while maintaining low resistance. Designed to eliminate dust particles, pollen, mold, and other irritants, HEPA filters do more than just cleanse the air; they safeguard our health and nourish our lungs.
Hence, HEPA filters find their applications across a plethora of industries. The food and beverage sector relies on them to maintain pristine conditions, essential for both food safety and quality. In LCD manufacturing, where even the minutest of dust particles could lead to costly defects, HEPA filters ensure optimal production environments. Their role extends to the healthcare industry as well, where clean air is vital for a patient's wellbeing.
The electronics, precision instrument, and chemical industries have all adopted HEPA filters as their trusted allies. Instruments of precision cannot tolerate the slightest semblance of dust; electronics require clean environments for efficient working, and the chemical industry employs HEPA filters to trap hazardous particulates suspended in the air.

However, there is something else that sets HEPA filters apart - their endurance. While they can operate tirelessly in conditions up to 70℃, it is their capacity to champion the cause of clean air across varying industries that truly testifies their adaptability.
In conclusion, the HEPA filter is a quintessential symbol of human ingenuity responding to the essential need for clean air. As we move forward, wrestling with the challenges of pollution and ill-effects of impure air, it is tools like the HEPA filter that elevate our odds, making not just our environments, but our lives significantly better. The promise of a cleaner, healthier tomorrow rests, to a considerable extent, on this unsung hero's remarkable shoulders
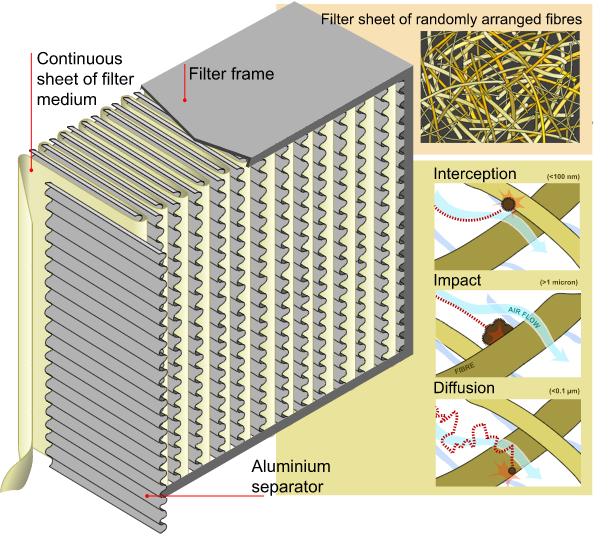
HEPA (High Efficiency Particulate Air) filters operate based on a combination of mechanisms to cleanse the air of particles.
Interception: As air flows through the filter, particles traveling within the airstream come within one particle radius of a fiber. These particles are captured and embedded into the fiber.
Impaction: Larger particles are unable to avoid fibers by following the curving contours of the airflow and are forced to embed in one of them directly; this effect increases with diminishing fiber separation and higher airflow velocity.
Diffusion: An enhancing mechanism that is a result of the collision with gas molecules by the smallest particles, especially those below 0.1 µm in diameter, which are thereby impeded and delayed in their path through the filter. This action enhances the probability that particles will be stopped by either of the two mechanisms above; it becomes dominant at lower airflow velocities.
Sieving: Depending on the gap between the filter fibers, some particles larger than this gap may also be trapped.
High-speed air movement through the HEPA filter separates out particles via these physical mechanisms, leading to a tremendous reduction in particle count on the downstream side of the filter. After being retained in the filter media, the air void of harmful particulates is then released back into the environment, resulting in cleaner, healthier air.
This combination of mechanisms is what enables HEPA filters to be so effective, removing up to 99.995% of particles greater than 0.3μm. It's important to note that the filter's effectiveness will depend on the speed of the air as it moves through the filter, as well as the size and nature of the particles.
The performance of a HEPA (High Efficiency Particulate Air) filter can be influenced by various factors:
Particle Size: While HEPA filters are extremely efficient at removing particles, their efficiency can vary with particle size. They are typically most effective at removing particles around 0.3 micrometers in size, but may be less effective at removing extremely small or large particles.
Air Flow Rate: The speed at which air travels through the filter can impact its performance. If the air moves too quickly, particles may not be exposed to the filter long enough to be captured. Conversely, if the air moves too slowly, particles can settle and build up on the filter, potentially clogging it over time.
Filter Maintenance: Over time, a build-up of particles can clog the filter, reducing its effectiveness. Hence, regular maintenance and replacement is critical for optimal performance of a HEPA filter.
Air Leaks: If unfiltered air can bypass the filter due to a poor seal or damage to the filter itself, this reduces the overall effectiveness of the filter.
Humidity and Temperature: Both these factors can affect the physical properties of particles and fibers in the filters, potentially impacting the effectiveness of a HEPA filter.
By understanding these factors, users of HEPA filters can ensure optimal performance and air quality by regularly maintaining and replacing their filters, and ensuring they are properly installed and sealed.
Humidity and temperature can have a significant effect on the performance of a HEPA filter and here's how:
Humidity: High levels of humidity can cause certain types of particles to expand or clump together. This might make them easier to trap, but it could also potentially clog the filter more quickly. Alternatively, if the particles clump together to form a size smaller than the filter's minimum efficiency size (around 0.3 micrometers), they may evade filtration. Furthermore, consistent exposure to high humidity can degrade the filter materials over time, reducing their overall performance and lifespan.
Temperature: Extreme temperatures, both high and low, can affect the physical properties of the filter materials. For instance, high temperatures may cause the filter fibers to become brittle and break, thus decreasing the filter's efficiency. On the other hand, extremely low temperatures might render the filter media brittle or otherwise impact performance.
It’s crucial to remember that not all HEPA filters are alike. Some are designed to withstand higher levels of humidity and broader temperature ranges than others, so it's essential to understand the specifications and operating conditions for your particular filter.